iOS Safe Area
In iOS 7 Apple introduced
topLayoutGuide and bottomLayoutGuide as properties of UIViewController. They allowed you to create constraints to keep your content from being hidden by UIKit bars like the navigation, status or tab bar. It’s now replaced by Safe area layout guide in iOS 11. If you want to know more about difference between these check out the link below
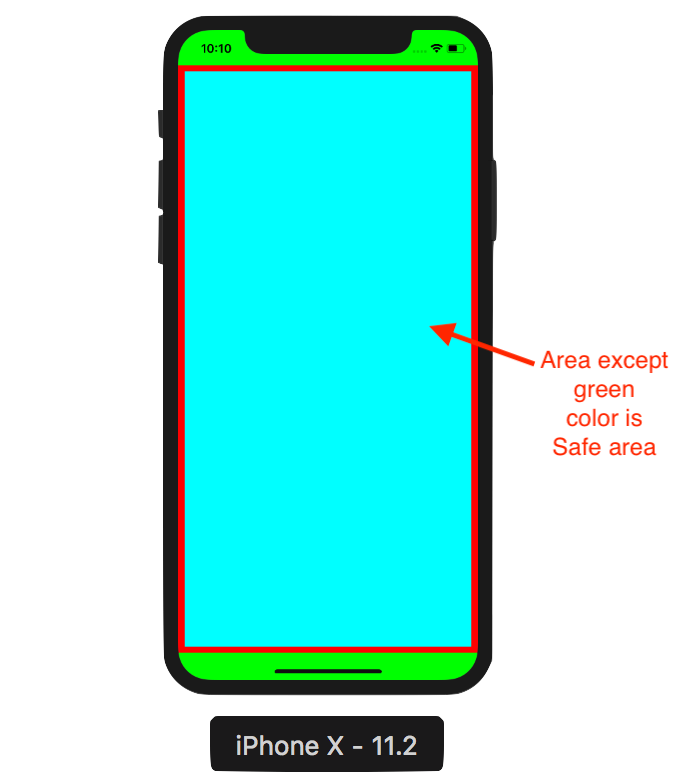
Safe Area layout guide: The layout guide representing the portion of your view that is unobscured by bars and other content. Initially when view is not visible on screen the layout guide edges are equal to the edges of the view. This guide reflects the portion of the view that is not covered by navigation bars, tab bars, toolbars, and other ancestor views. Once view appears it automatically update constraints which is great benefit for us.
Below example will help you to understand how safe area layout guides are used in efficient way.
Below snippet shows layout creation using Safe Area Layout Guide:
| class ViewController: UIViewController { | |
| let wrapperView = UIView() | |
| let cyanView = UIView() | |
| override func viewDidLoad() { | |
| view.backgroundColor = .yellow | |
| view.addSubview(wrapperView) | |
| wrapperView.addSubview(cyanView) | |
| wrapperView.backgroundColor = .red | |
| wrapperView.translatesAutoresizingMaskIntoConstraints = false | |
| cyanView.backgroundColor = .cyan | |
| cyanView.translatesAutoresizingMaskIntoConstraints = false | |
| applyConstraints() | |
| } | |
| func applyConstraints() { | |
| let guide = view.safeAreaLayoutGuide | |
| wrapperView.topAnchor.constraint(equalTo: guide.topAnchor).isActive = true | |
| wrapperView.leadingAnchor.constraint(equalTo: guide.leadingAnchor).isActive = true | |
| wrapperView.trailingAnchor.constraint(equalTo: guide.trailingAnchor).isActive = true | |
| wrapperView.bottomAnchor.constraint(equalTo: guide.bottomAnchor).isActive = true | |
| let margins = wrapperView.layoutMarginsGuide | |
| cyanView.topAnchor.constraint(equalTo: margins.topAnchor).isActive = true | |
| cyanView.leadingAnchor.constraint(equalTo: margins.leadingAnchor).isActive = true | |
| cyanView.trailingAnchor.constraint(equalTo: margins.trailingAnchor).isActive = true | |
| cyanView.bottomAnchor.constraint(equalTo: margins.bottomAnchor).isActive = true | |
| } | |
| } |
There are 2 ways to use SafeAreaLayoutGuide: Either align with `equalTo` or `constraintEqualToSystemSpacingBelow` to topAnchor. When we use `constraintEqualToSystemSpacingBelow` the distance between two anchors is determined by multiplying the system space by the value in the
multiplierparameter. System space is most of time 8 pixel which also depends on other factors. For eg. if the anchors represent text baselines, the spacing is determined by the fonts used at those baselines.| import UIKit | |
| class ViewController: UIViewController { | |
| let wrapperView = UIView() | |
| let cyanView = UIView() | |
| override func viewDidLoad() { | |
| view.backgroundColor = .green | |
| view.addSubview(wrapperView) | |
| wrapperView.addSubview(cyanView) | |
| wrapperView.backgroundColor = .red | |
| wrapperView.translatesAutoresizingMaskIntoConstraints = false | |
| cyanView.backgroundColor = .cyan | |
| cyanView.translatesAutoresizingMaskIntoConstraints = false | |
| } | |
| override func viewDidLayoutSubviews() { | |
| wrapperView.frame = CGRect(x: view.frame.origin.x, | |
| y: view.safeAreaInsets.top, | |
| width: view.frame.size.width, | |
| height: view.frame.size.height - view.safeAreaInsets.top) | |
| cyanView.frame = CGRect(x: wrapperView.layoutMargins.left, | |
| y: wrapperView.layoutMargins.top, | |
| width: wrapperView.frame.size.width - wrapperView.layoutMargins.left-wrapperView.layoutMargins.right, | |
| height: 100) | |
| } | |
| } |
Below snippet shows layout creation using Safe Area Insets:
| override var additionalSafeAreaInsets: UIEdgeInsets { | |
| set { | |
| super.additionalSafeAreaInsets = UIEdgeInsetsMake(10.0, 50.0, 10.0, 50.0) | |
| } | |
| get { | |
| return UIEdgeInsetsMake(10.0, 50.0, 10.0, 50.0) | |
| } | |
| } |

Comments
Post a Comment